26+ Plant Cell Amyloplast Function
Apart from storing starch mayloplasts are gravity sensors in. Web Plastids are pivotal subcellular organelles that have evolved to perform specialized functions in plant cells including photosynthesis and the production and storage of metabolites.
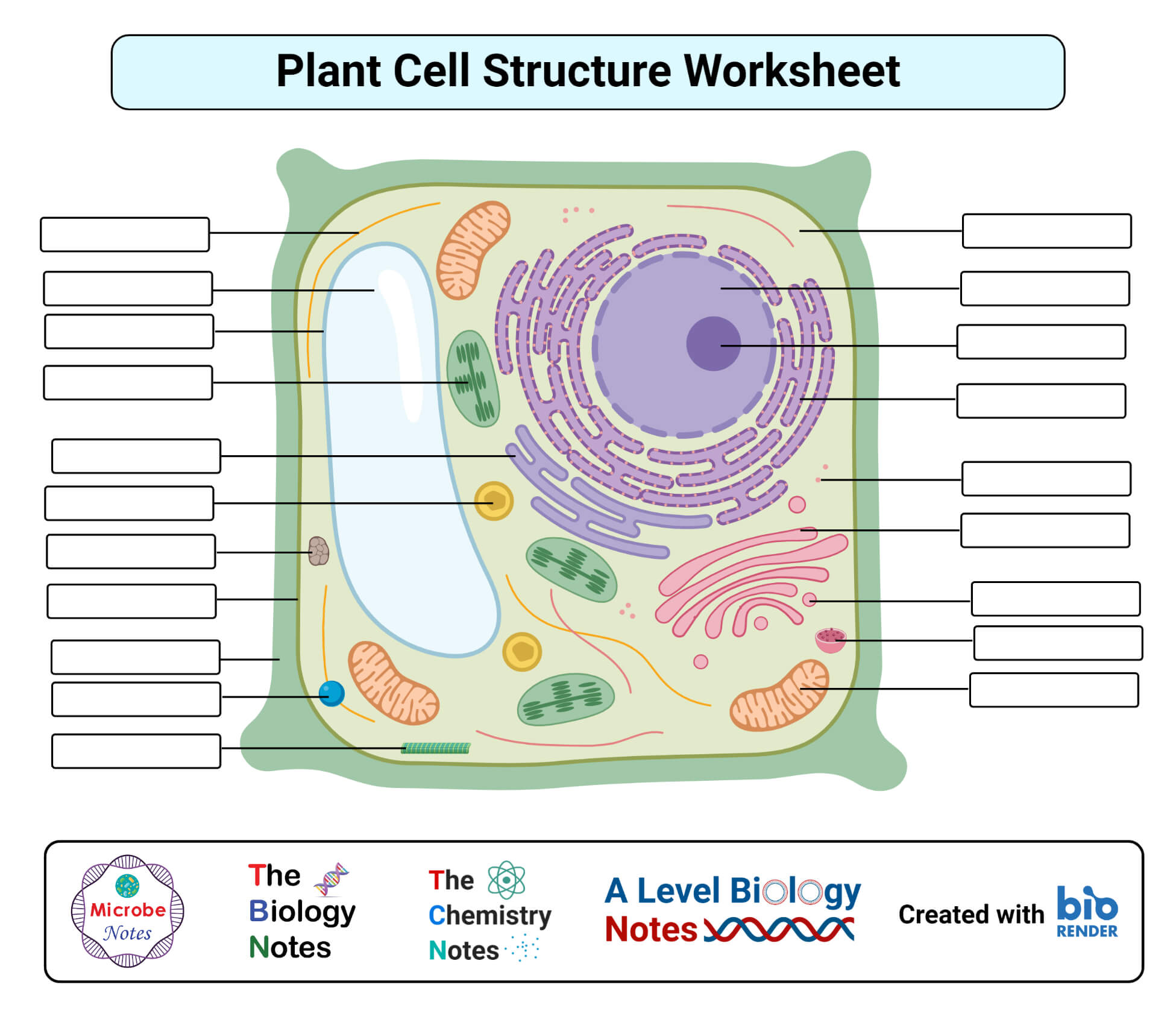
Plant Cell Definition Structure Parts Functions Labeled Diagram
Plastids are organelles found in the cells of plants.
. They have a double membrane and also have their own. Web Amyloplasts are non-pigmented organelles found in plant cells. Web In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research 1998.
Web Although plastids are common subcellular organelles in plants previous research has been a bias toward the photosynthetic plastids called chloroplasts or carotenoid enriched plastids called chromoplasts Cruz et. Amyloplasts are found in shoots and in specialized cells of the root cap. Web Plant cells are characterized by a unique group of interconvertible organelles called plastids which are descended from prokaryotic endosymbionts.
The most studied plastid type is the chloroplast which carries out the ancestral plastid function of. D Diagram of an endodermal cell. Web An amyloplast is an organelle found in plant cells.
Web Amyloplast is one of the best-studied plastids. When a plant is tilted the statoliths drop to. Web Amyloplasts in special tissues in the stem the endodermis and the root the columella of the root cap perform a mechanical not a metabolic function as they sink to the bottom of the cell and signal an upperlower cell polarity that initiates a gravitropic growth response Toyota et al 2013.
Web What is the function of amyloplast in a plant cell. Web However due to the presence of the cell wall plant root endodermal cells cannot establish direct tight junctions like gut epithelial cells. Web The amyloplast a specialized organelle is the major site for starch synthesis and storage in wheat grain.
It is known for synthesising starch through polymerisation or joining glucose molecules and plays an essential role in gravitropism. Web Amyloplast is a double-membraned plastid found in the non-photosynthesising parts of the plants like the roots. Web Plastids are essential for a wide range of normal plant cell functions and so have a number of specialist forms.
All the stored starch in a cell can be found in plastids as starch granules. Encyclopedia of Cell Biology 2016 Actin. Starch in the Gravitational Response of Roots and Stems.
Plants have developed a unique cell wall structure. Amyloplasts are plastids that produce and store starch within internal membrane compartments. Shoots exhibit negative gravitropism and grow.
The amyloplast definition is an organelle that produces and stores starch within the. Amyloplasts are sites for the synthesis and bulk storage of starch and are found in roots and storage organs such as cotyledons seed endosperm and tubers. Understanding the metabolism in amyloplast during grain development in wheat cultivars with different quality traits will provide useful information for potential yield and quality improvement.
Amyloplasts are specialized in this role and contain large depots of starch. Which is the best definition of an amyloplast. Google Scholar Suzuki M.
Web An amyloplast is a type of leucoplast that develops from a proplastid. Web We propose that amyloplasts fulfill a more complex function by interacting with a receptor which is a nucleus in transduction of some signal to it. They are commonly found in vegetative plant tissues such as tubers potatoes and bulbs.
Web A Five-week-old plant of Col-0 ecotype. Amyloplasts are found in roots and storage tissues and they store and synthesize starch for the plant through the polymerization of glucose. Amyloplasts are specifically a type of leucoplast a subcategory for colorless non-pigment-containing plastids.
Web Amyloplasts are colorless plastids in plant cells that are responsible for the formation and storage of starch. Web Plants develop amyloplasts in storage organs such as the endosperm and tubers to biosynthesize and store glucose as starch. Learn about the definition function and placement of amyloplasts and.
Sedimentation of amyloplasts within the cell has been correlated with the capacity of the plant to perceive gravity. Starch is produced in the matrix space stroma of amyloplasts and. B C Schematic structure of an inflorescence stem.
Web Amyloplasts in special tissues in the stem the endodermis and the root the columella of the root cap perform a mechanical not a metabolic function as they sink to the bottom of the cell and signal an upperlower cell polarity that initiates a gravitropic growth response Toyota et al 2013. Its a type of leucoplast primarily involved in the synthesis and storage of starch the word Amylo means starch. It is involved in different metabolic pathways in a plant.
Web I n plant cells amyloplasts synthesize starch Figure 2. It is located in plant cells. They come in a variety of forms with different characteristics enabling them to function in a diverse array of organtissuecell-specific developmental.
Web Amyloplasts are a type of plastid double-enveloped organelles in plant cells that are involved in various biological pathways. Web Amyloplasts also known as statoliths are specialized plastids that contain starch granules and settle downward in response to gravity. Their main function is to convert glucose into starch through the process of polymerization.
This signaling process takes place in the gravity-sensing cells which is currently designated as gravity signaling. Gravity-induced statolith movement in certain order leads to a new functional connection between gravity susceptors--amyloplasts and a receptor--a nucleus receiving some signal presumedly of a. They can be found in different types of plant cells including those found in the tubers root caps and storage tissues as well as the cotyledon.
Web Amyloplasts are specifically a type of leucoplast a subcategory for colorless non-pigment-containing plastids. Web The relocation of amyloplasts elicits a biological signaling pathway that promotes directional auxin transport from the gravity-sensing cells to the lower flank of the gravity-responsive organ. The buoyant mass of amyloplasts present in specialized cells in the center of the root cap and in the stem depending on the plant.

The Illuminated Plant Cell Trends In Plant Science
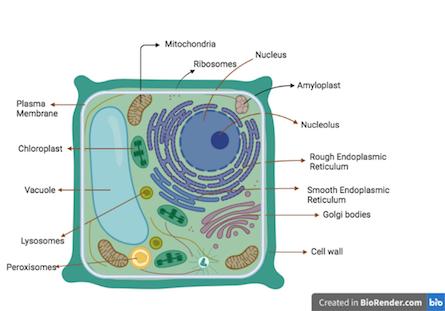
What Is A Plant Cell Definition Diagram And Structure
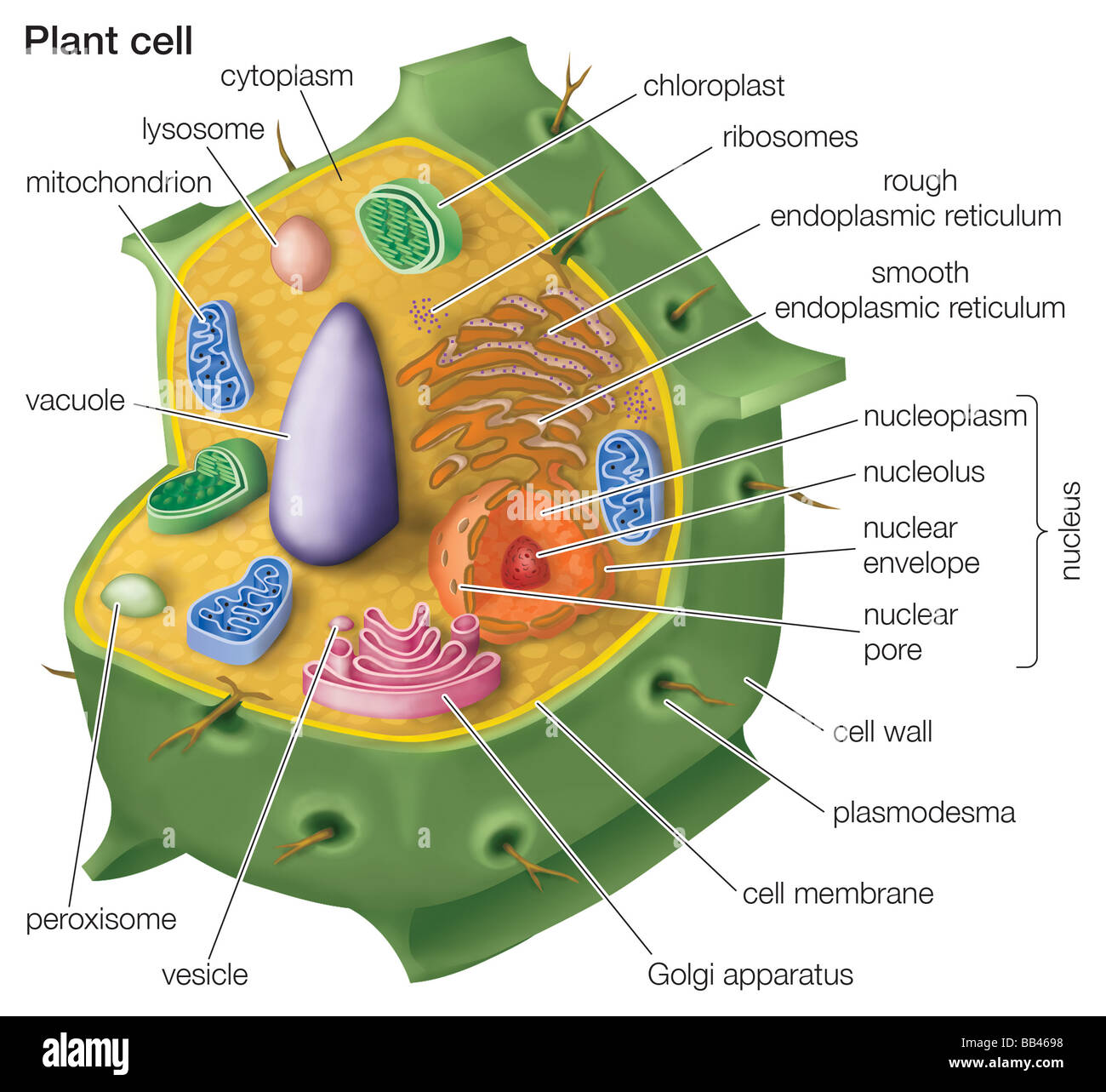
Eukaryotic Plant Cell Hi Res Stock Photography And Images Alamy
What S The Function Of An Amyloplast Quora

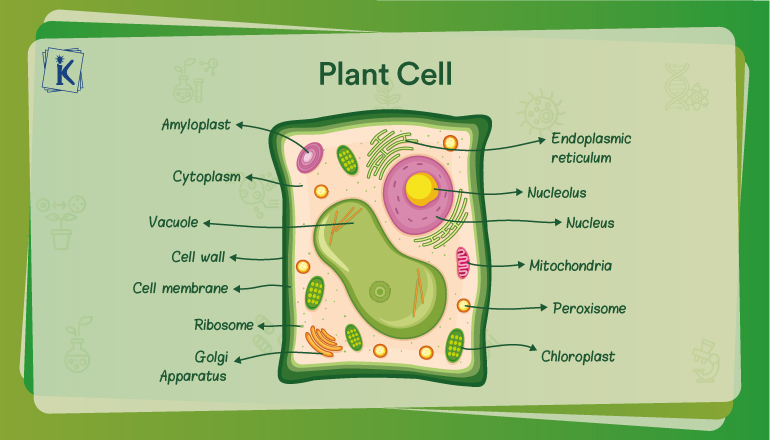
Plant Cell Definition Structure Types Diagram Function Plato Online

Amyloplast An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Plant Cell Diagram Quizlet
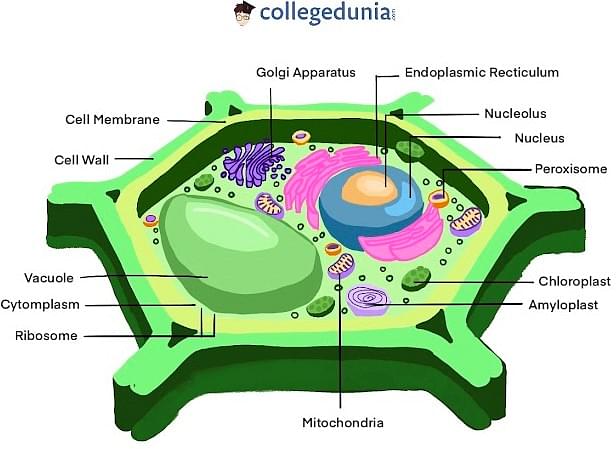
Plant Cell Definition Structure Function Diagram Types

Structure And Function Of The Plant Cell Explained Organelles Youtube
What S The Function Of An Amyloplast Quora
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/amyloplast-5b6c5498c9e77c0050442e0c.jpg)
Amyloplast Definition And Function
What S The Function Of An Amyloplast Quora

Cells Plant Specialists
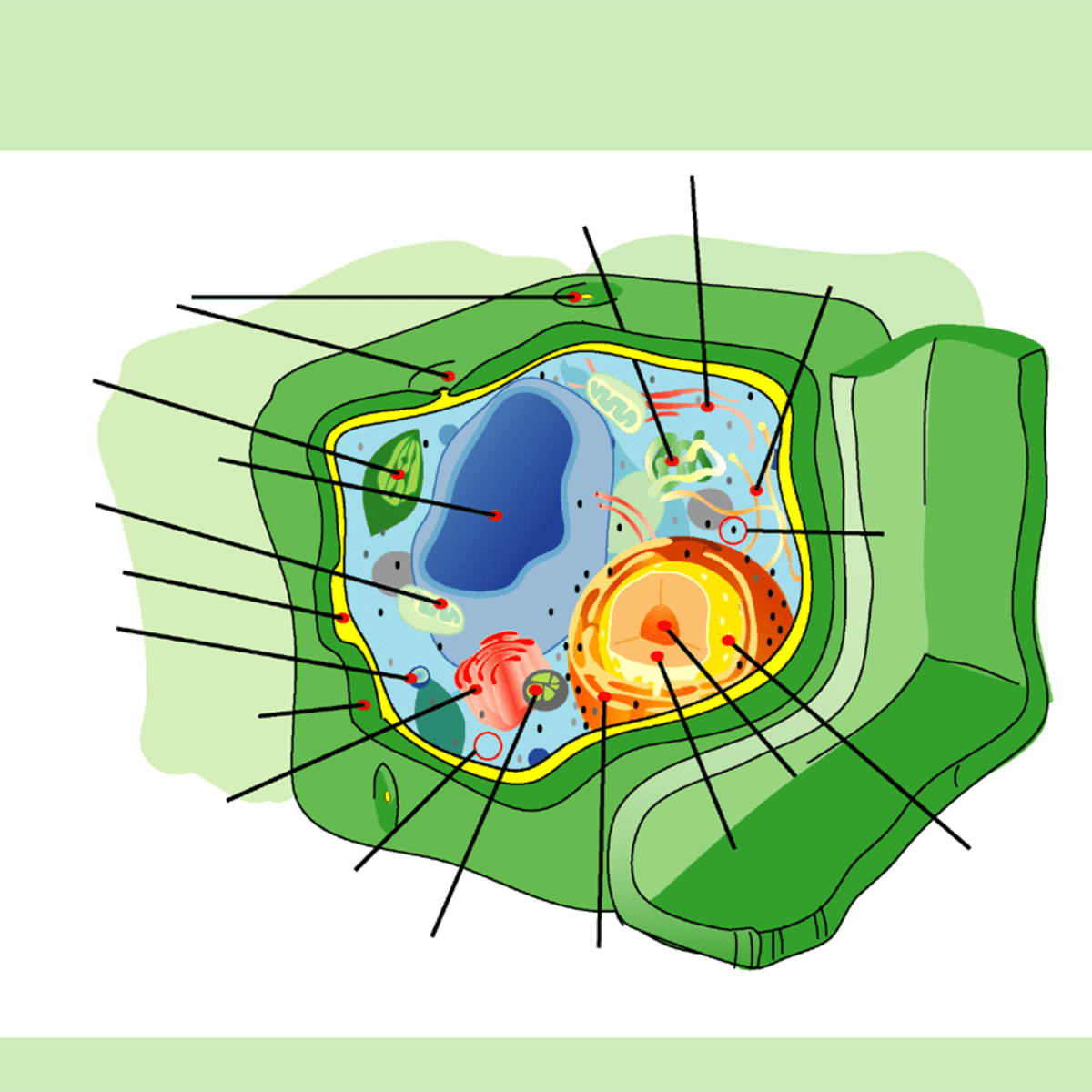
Structure Of A Plant Cell A Visual Guide Owlcation
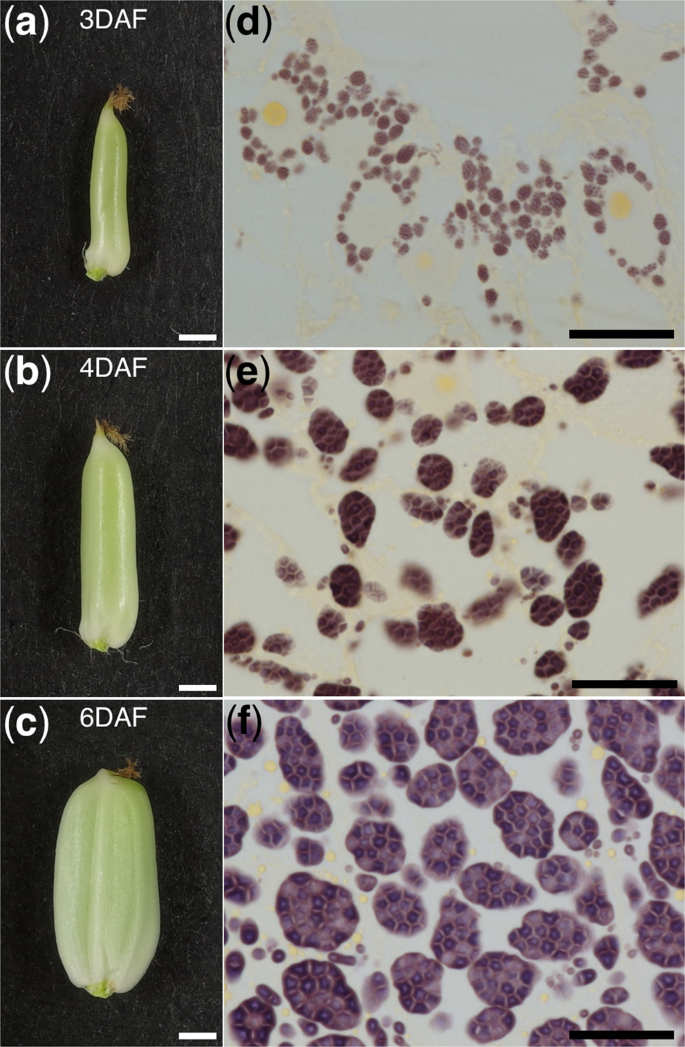
Imaging Amyloplasts In The Developing Endosperm Of Barley And Rice Scientific Reports

The Plant Cell 13 Key Structures Youtube

What Are Amyloplasts What Functions Do They Have Quora